In this article, you’ll learn to generate text files from MATLAB using the MATLAB command fprintf. You’ll find out about:
- The MATLAB fprintf Syntax
- How to print a matrix in a text file
- How to print complex numbers in a text file
MATLAB fprintf Syntax
How to use fprintf in MATLAB
In MATLAB, you can print text into a file by using the fprintf MATLAB command. To do this, go through the following 3 steps:
- Open a file using fopen.
- Write content using fprintf.
- Close the file using fclose.
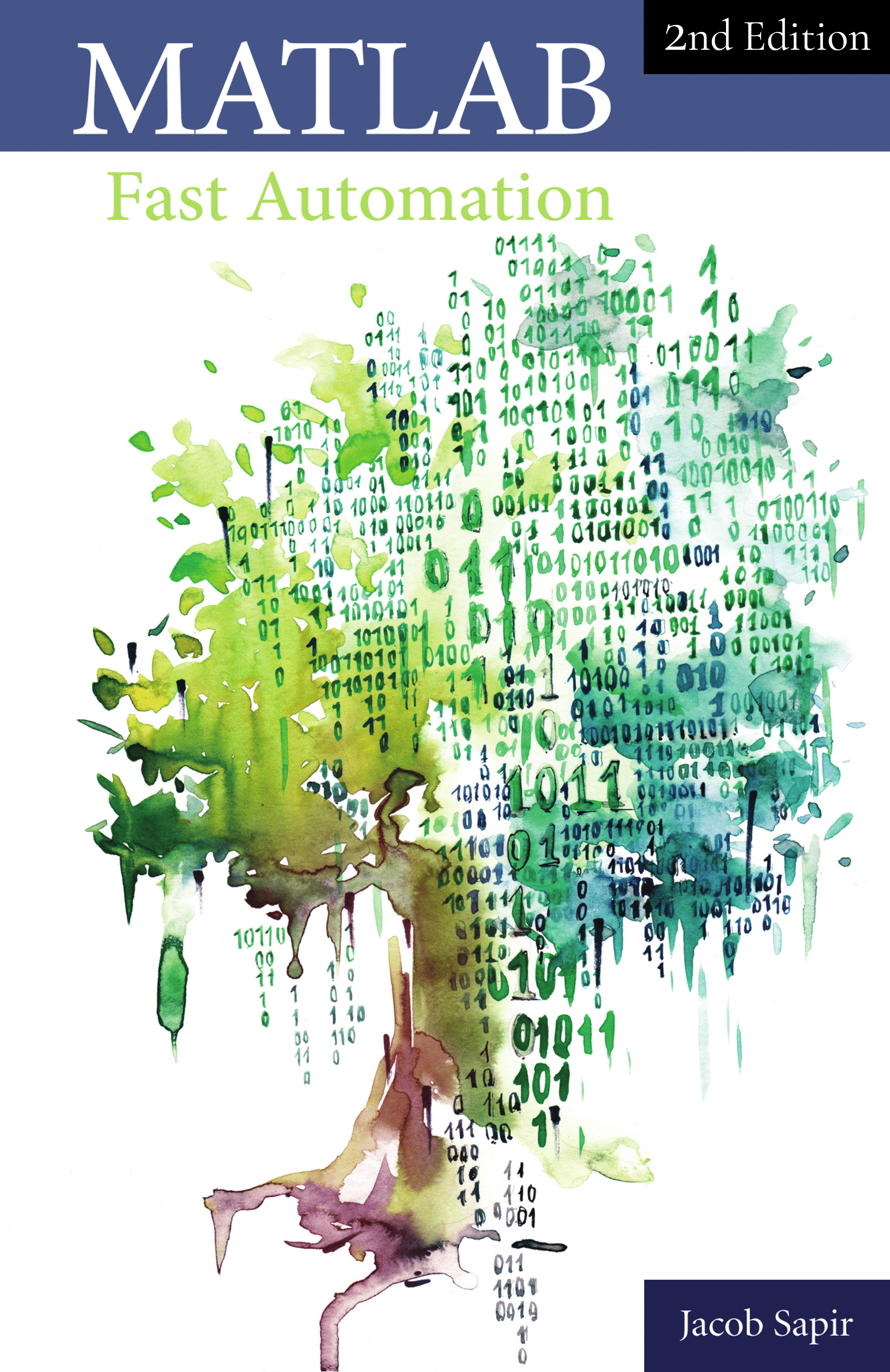
For example, let’s write the word “Text” into a file named “textFileName.txt”:
fid = fopen('textFileName.txt', 'at'); fprintf(fid, 'Text'); fclose(fid);
- fid: output of the fopen command, required to reference the file on which to write on (and to write on different files at once).
- fopen(‘textFileName.txt’, ‘at’): open or create (if it doesn’t exist) a file named “textFileName.txt’
- “a” is for appending data to the end of the file
- “t” is for opening the file in text mode
- fprintf(fid, ‘Text’): print the word ‘Text’ into the file referenced by the “fid” variable.
- fclose(fid): close the file referenced by the “fid” variable.
If you run this piece of code in MATLAB, a file named ‘textFileName.txt’ will be created in your current folder:
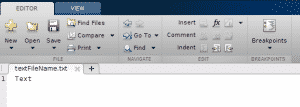
Delete Existing Content When Writing
There are 2 ways to delete the content before writing when the file already exists:
- Either use the argument ‘w’ instead of ‘a’ in the fopen MATLAB command:
fid = fopen('textFileName.txt', 'wt'); fprintf(fid, 'Text'); fclose(fid);
- Or, use the delete MATLAB command to delete the existing file before using fopen to create a new file with the same name:
delete('textFileName.txt'); fid = fopen('textFileName.txt', 'at'); fprintf(fid, 'Text'); fclose(fid);
If ‘textFileName.txt’ doesn’t exist, MATLAB will generate a warning; otherwise, it will delete the file before creating a new one with fopen.
Print Numbers in a Text File
You can format as follows:
delete('textFileName.txt'); fid = fopen('textFileName.txt', 'at'); fprintf(fid, ['%d + %d = %d'], 2, 3, 5); fclose(fid);
Or, you can just use the num2str MATLAB command to convert your number into a text:
delete('textFileName.txt'); fid = fopen('textFileName.txt', 'at'); fprintf(fid, [num2str(2) '+' num2str(3) '=' num2str(5)]); fclose(fid);
Warning: File not Found or Permission Denied
When you encounter a warning saying that the file cannot be overwritten, it could be because there have been some issues with closing the file the last time it was opened:
![]()
In this case, you can close it by using:
fclose all
After running this command you should be able to delete/overwrite the file.
MATLAB fprintf: Matrix
Let’s say we have a matrix:
\(m = \begin{pmatrix}1 & 2 & 3\\4 & 5 & 6\end{pmatrix}\)
It can be defined in MATLAB as follows:
m = [1 2 3 ; 4 5 6];
The intuitive way to write a matrix would be to use “%d” for each column of the matrix such as:
fid = fopen('textFileName.txt', 'at'); fprintf(fid, '%d %d %d\n', m); fclose(fid);
However, because fprintf doesn’t store matrices in an intuitive way, in MATLAB you’d get:
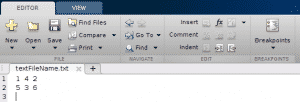
Instead, you need to use the transpose of that matrix:
fid = fopen('textFileName.txt', 'at'); fprintf(fid, '%d %d %d\n', m'); % notice the single quotation mark at the right of m fclose(fid);
Now, you get:
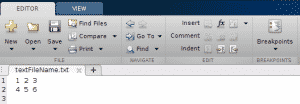
MATLAB fprintf: Complex Number
If you want to print complex numbers, there is no specific format, you need to separate the real from the imaginary part:
x = 1+3i; fid = fopen('textFileName.txt', 'at'); fprintf(fid, '%d+%dj\n', real(x), imag(x)); fclose(fid);
Here’s what the text file will look like:
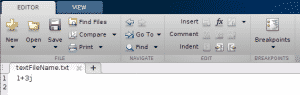
Key takeaways:
- The basic structure to write text into a file is the following:
fid = fopen(fileName, 'at'); % a is for append fprintf(fid, text); fclose(fid);
- To delete the content in the file before writing using the syntax:
- Use “w” as an argument of fopen:
fid = fopen(fileName, 'wt'); % w is for write fprintf(fid, text); fclose(fid);
- Use the delete MATLAB command:
delete(fileName); fid = fopen(fileName, 'at'); fprintf(fid, text); fclose(fid);
- Use “w” as an argument of fopen:
- To print a matrix in MATLAB, you need to transpose the matrix:
fid = fopen('textFileName.txt', 'at'); fprintf(fid, '%d %d %d\n', m'); % notice the single quotation mark at the right of m fclose(fid);
- To print a complex number in MATLAB, separate the real from the imaginary part:
x = 1+3i; fid = fopen('textFileName.txt', 'at'); fprintf(fid, '%d+%dj\n', real(x), imag(x)) fclose(fid);
To learn more about fprintf, check out the following links:
- A real-life example of writing model information in a file: https://realtechnologytools.com/fprintf-matlab/
- MathWorks documentation: https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/fprintf.html
If you want to learn more about the tools that helped me stop wasting time doing mindless work (such as generating Excel reports, Word documents, or creating clean and simple user interfaces) I wrote a small reference book about it:

